Block cipher -
is one of the two common modern symmetric cipher types. It is distinguished from a stream cipher, because a b
lock cipher performs operations on a chuck or blocks of plain text at once, whereas a stream cipher can operate on a single bit
of plaintext at a time. The generated ciphertext has blocks equal to the number of blocks in plaintext and also has the same number of
bits in each block as of plain text. Block cipher uses a symmetric key (the same key for encryption and decryption.
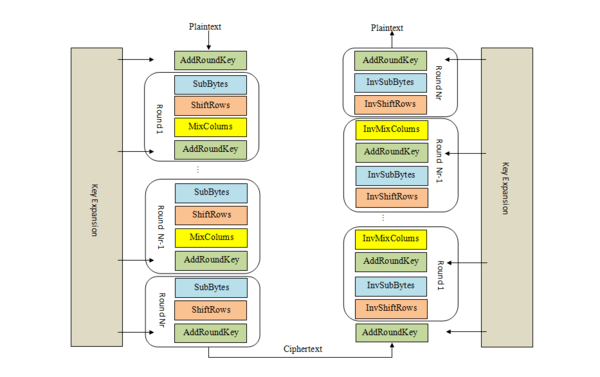
The foremost example of a modern block cipher is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) . AES is the primary cipher approved for use
by the U.S. government to protect electronic data. It was certified in 2001, and has been something of a de facto standard cryptographic
algorithm worldwide. It replaced the aging DES, also a block cipher, which was issued in 1977 . There are too many block ciphers to list
them all, but DES and AES are the two most famous examples..
AES, encrypts 128 bit blocks with a key of predetermined length: 128, 192, or 256 bits.
DES divides the plain text into the number of blocks, each of 64-bit. DES operates on one block of plain text at a time.
Key of 56-bit is applied to each block of plain text to produce its corresponding ciphertext of 64-bit.
During decryption also only one block of ciphertext is operated at a time to produce its corresponding block plain text.
In DES the decryption algorithm is the same as the encryption one.
w o t r e m o o l e j c p e
c g t a f p