Universal serial bus, USB is a hardware interface that allows peripheral devices (like digital cameras, PDAs, MP3 players, keyboards, computer mice, printers and scanners) to connect to – and interact with – a host device (i.e. a personal computer).
Common USB device includes:
Digital Camera, External drive, iPod or other MP3 players, Keyboard, Keypad, Microphone, Mouse, Printer, Joystick, Jump drive aka Thumb drive, Scanner, Smartphone , Tablets, Webcams
USB serves two main functions:
The Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a specification developed by Compaq, Intel, Microsoft and NEC, joined later by Hewlett-Packard, Lucent and Philips. These companies formed the USB Implementers Forum, Inc as a non-profit corporation to publish the specifications and organise further development in USB.
The aim of the USB-IF was to find a solution to the mixture of connection methods to the PC, in use at the time. We had serial ports, parallel ports, keyboard and mouse connections, joystick ports, midi ports and so on. And none of these satisfied the basic requirements of plug-and-play. Additionally many of these ports made use of a limited pool of PC resources, such as Hardware Interrupts, and DMA channels.
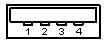
So the USB was developed as a new means to connect a large number of devices to the PC, and eventually to replace the 'legacy' ports. It was designed not to require specific Interrupt or DMA resources, and also to be 'hot-pluggable'. It was important that no special user-knowledge would be required to install a new device, and all devices would be distinguishable from all other devices, such that the correct driver software was always automatically used.USB cable connectors and ports are based on a 4-pin arrangement, which means that data and power transfer take place over four distinct wires, which are integrated within each USB cable.
Of these 4 wires, two are dedicated to sending and receiving data, The signals on these two wires are referenced to the (third) GND wire, the fourth is called VBUS, and carries a nominal 5V supply, which may be used by a device for power, Each wire has a designated color for easy identification.
Standard USB Pinout Chart:
| Pin | Wire Color | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red | VCC | +5V |
| 2 | White | D- | Data- |
| 3 | Green | D+ | Data+ |
| 4 | Black | GND | Ground |
Mini USB Pinout Chart:
| Pin | Wire Color | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red | VCC | +5V |
| 2 | White | D- | Data- |
| 3 | Green | D+ | Data+ |
| X | ID | Varies* | |
| 4 | Black | GND | Ground |
*Pin “X” can vary by cable or application. In some cases, Pin “X” isn’t connected at all. When it is connected, this wire can either be attached to the ground, or used to identify and/or indicate the presence of an attached peripheral device.
USB Specification
The USB specification defines three data speeds; Low Speed(at 1.5Mbit/s),Full Speed(at 12Mbit/s)High Speed(at 480Mbit/s),
Two important aspects of the USB are its support capability and total bandwidth. It is capable of supporting 127 devices and has a total bandwidth of 12 Mbit per second which is equal to 1.5 MB per second.
Since 1MB = 8Mbits , therefore : 1.5MB = 12Mbits
Working of a 12 Mbit (full speed device) or a 1.5 Mbit (low speed devices) depends on the total bandwidth of the USB.
USB transfer speeds
The USB specification defines three data speeds; Low Speed(at 1.5Mbit/s), Full Speed(at 12Mbit/s)High Speed(at 480Mbit/s),
The Different USB Connectors Types and Signaling Rates
USB 1.x is an external bus standard that supports data transfer rates of 12 Mbps and is capable of supporting up to 127 peripheral devices. It was introduced in 1996 and initially supported a Low-Speed transfer rate at 1.5 Mbps. This specification was later revised in 1998 to USB 1.1, also known as Full-Speed USB. This updated specification supports a bandwidth of 12 Mbps and power levels up to 2.5W. USB connectors supporting this spec include USB Type-A and USB Type-B.
USB 2.0, also known as hi-speed USB, was developed by Compaq, Hewlett Packard, Intel, Lucent, Microsoft, NEC, and Phillips and was introduced in 2001. Hi-Speed USB is capable of supporting a transfer rate of up to 480 megabits per second (Mbps), or 60 megabytes per second (MBps). In 2001, the USB 2.0 specification was introduced. USB 2.0, also known as High-Speed USB, supports a transfer rate of 480 Mbps and is backwards compatible with USB 1.1. It also uses the same USB Type-A and USB Type-B cables and connectors, as well as the same software interfaces as USB 1.1, but substantially increases the support for higher bandwidth peripheral devices, such as video camera devices.
USB 3.0, also known as SuperSpeed USB, was first made available in November 2009 by Buffalo Technology, but the first certified devices weren't available until in January 2010. USB 3.0 improved upon the USB 2.0 technology with speed and performance increases, improved power management and increased bandwidth capability. It provides two unidirectional data paths for receiving and sending data at the same time. USB 3.0 supports transfer rates up to 5.0 gigabits per second (Gbps), or 640 megabytes per second (MBps). Following the release of USB 3.1, it's officially renamed to "USB 3.1 Gen1" for marketing purposes. The first certified devices included motherboards from ASUS and Gigabyte Technology. Dell began including USB 3.0 ports in their Inspiron and Dell XPS series of computers in April 2011.
USB 3.1, also known as SuperSpeed+, was made available as of July 31, 2013, and is the latest version of the USB protocol. USB 3.1 is capable of transfer rates of up to 10 Gbps, putting it in line with the first generation of Apple's Thunderbolt channel. Today, many devices use the USB 3.0 and 3.1 revisions for improved performance and speed.
USB 3.2
In 2017, USB 3.2 was released, further increasing the signaling rate. This revision supports USB transfer rates up to 20 Gbps, which is possible due the specification signaling
10 Gbps over 2 lanes in a USB Type-C cable.
Throughout the years, there have been numerous updates to the naming conventions and branding of the various releases of USB 3.0, USB 3.1 and USB 3.2. Today, USB 3.2 encompasses all prior USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 specifications, supporting signaling rates at 5 Gbps, 10 Gbps, and 20 Gbps.
USB 3.0 is now USB 3.2 Gen 1 (SuperSpeed USB) and has a maximum throughput of 5 Gbps
USB 2.0 has a maximum signaling rate of 480 Mbit/s and USB 3.0 has a usable data rate of up to 4 Gbit/s (500 MB/s).
USB4
The USB4 specification was released in 2019 and offers users some of the most robust features and capabilities, including the ability to transfer data up to 40 Gbps using a dual-lane operation within a Type-C cable. USB4 permits the highest USB bandwidth available with multiple data and display protocols to efficiently share the maximum aggregate bandwidth over the bus. USB4 also has backwards compatibility with USB 3.2, USB 2.0, and Thunderbolt.
USB version compatibility
Each version of USB port is backward compatible and forward compatible, meaning it can support any version below or above its current number. For example, devices designed with USB 1.1 and 2.0 technology work in a 3.0 port. However, it should be noted that devices with lower versions run at their native transfer speeds even though USB 3.0 is capable of higher. Similarly, if you connect a USB 3.1 device into a USB 2.0 port, the 3.1 device's max transfer rate is limited to that of the 2.0 port.
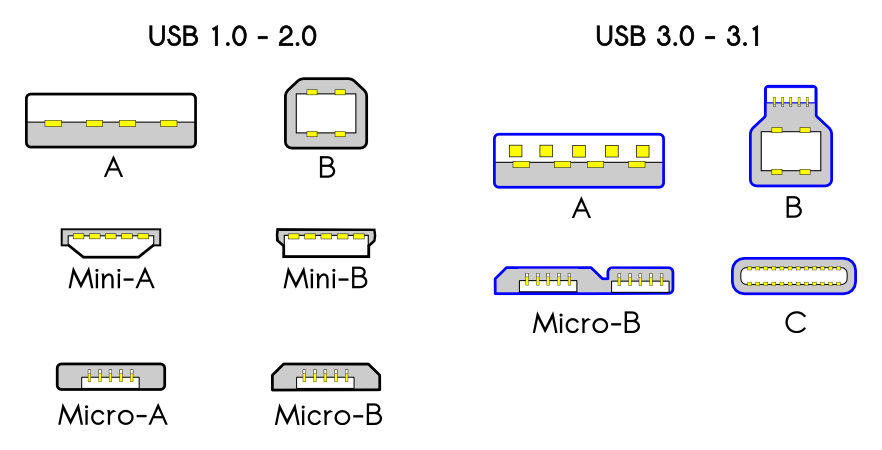
What are the Different USB Connector Types?
USB cables and connectors create an interface as a way for computers and peripheral devices to connect with each other and transfer data. There are numerous USB connector types that have been used to interface the USB 1.1/2.0 and USB 3.0 protocols. Some of the most commonly used connectors include USB Standard-A, USB Standard-B, USB Mini-B, USB Micro-B, and USB Type-C.
The term “USB type” can mean three different things:
In the case of 1 and 2, the type describes the physical shape of the connectors or ports. This cable would plug into two ports that have these shapes:
All devices have an upstream connection to the host and all hosts have a downstream connection to the device. Upstream and downstream connectors are not mechanically interchangeable, thus eliminating illegal loopback connections at hubs such as a downstream port connected to a downstream port. There are commonly two types of connectors, called type A and type B which are shown below.
Type A plugs always face upstream. Type A sockets will typically find themselves on hosts and hubs. For example type A sockets are common on computer main boards and hubs. Type B plugs are always connected downstream and consequently type B sockets are found on devices.
It is interesting to find type A to type A cables wired straight through and an array of USB gender changers in some computer stores. This is in contradiction of the USB specification. The only type A plug to type A plug devices are bridges which are used to connect two computers together. Other prohibited cables are USB extensions which has a plug on one end (either type A or type B) and a socket on the other. These cables violate the cable length requirements of USB.
Although a cable has two differently shaped connectors, the type is whichever end of the cable isn’t the standard USB Type-A connector. So, for example, a cable with both a USB Type-A and a Type-C connector is a USB Type-C cable.
If both connectors are USB Type-A, it would be a USB Type-A cable (or a USB male to male cable or, simply, a USB cable).
An iPhone cable is described as an Apple Lightning cable, to correspond with the iPhone’s unique Lightning connector.
An Android cable is called a Micro-USB cable.
That’s because USB Type-A is the most commonly used USB port and connector so an alternative type is the most distinguishing feature.
These USB connectors are sometimes referred to as “male” connectors, as they plug into a “female” port. The different types of connector—shown by USB version—are as follows.
USB Type-A: Is the most widely used connector type. It is primarily used on host controllers in computers and hubs and is more commonly used as a downstream connection.
USB Type-B: is mainly used for connecting USB peripheral devices including printers and compact devices like mobile phones. It is commonly used as an upstream connection.
USB Type-C: is an advanced connector type that uses a reversible design, and is intended to replace other connectors in the hopes of there being one cable to function with a variety of different devices.
Mini connectors
USB Type-A Mini
USB Type-B Mini
Micro connectors
USB Type-A Micro
USB Type-B Micro